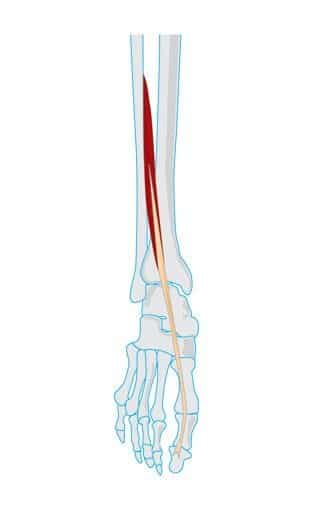
Extensor Hallucis Longus (EHL) Anatomy
This muscle is present on the front side of the lower leg and is involved in pulling the big toe upwards.
The large name actually indicates its function i.e. “Extensor” muscle that extends, “Hallucis” is big toe, known as Hallux in scientific terms and “longus” because it is the longer of the two extensor muscles of the big toe, (the other one is called Brevis). Simply, it is the long extensor muscle of the big toe.
Location:
This muscle is located in the anterior compartment of the lower leg. It starts from the inner side of the fibula. Fibula is the smaller of the two bones of the lower leg and is present on the outer side of the leg. This muscle originates from the lower half of the bone and also from the connective tissue membrane present between fibula and tibia.
Sometimes, at its origin, this muscle is united with another muscle called Extensor digitorum longus, the long extensor of the digits.
It is a thin muscle and as it descends, it converts into a tendon (thick fibrous band). This tendon shifts towards the inner (medial) side of the foot at the ankle. It then travels on inner side of the upper aspect of the foot.
This tendon finally inserts into the upper surface of big toe bone. The big toe consists of two bones called phalanges. This muscle inserts into the phalanx that is farthest from the body (present under the nail).